|
CSI-DSP
Version 1.0.0
CSI DSP Software Library
|
|
CSI-DSP
Version 1.0.0
CSI DSP Software Library
|
Functions | |
| void | csky_rfft_fast_f32 (csky_rfft_fast_instance_f32 *S, float32_t *p, float32_t *pOut, uint8_t ifftFlag) |
| Processing function for the floating-point real FFT. More... | |
| csky_status | csky_rfft_fast_init_f32 (csky_rfft_fast_instance_f32 *S, uint16_t fftLen) |
| Initialization function for the floating-point real FFT. More... | |
| csky_status | csky_cfft_radix4_init_f32 (csky_cfft_radix4_instance_f32 *S, uint16_t fftLen, uint8_t ifftFlag, uint8_t bitReverseFlag) |
| Initialization function for the floating-point CFFT/CIFFT. More... | |
| csky_status | csky_rfft_init_f32 (csky_rfft_instance_f32 *S, csky_cfft_radix4_instance_f32 *S_CFFT, uint32_t fftLenReal, uint32_t ifftFlagR, uint32_t bitReverseFlag) |
| Initialization function for the floating-point RFFT/RIFFT. More... | |
| csky_status | csky_rfft_init_q15 (csky_rfft_instance_q15 *S, uint32_t fftLenReal, uint32_t ifftFlagR, uint32_t bitReverseFlag) |
| Initialization function for the Q15 RFFT/RIFFT. More... | |
| csky_status | csky_rfft_init_q31 (csky_rfft_instance_q31 *S, uint32_t fftLenReal, uint32_t ifftFlagR, uint32_t bitReverseFlag) |
| Initialization function for the Q31 RFFT/RIFFT. More... | |
| void | csky_rfft_q15 (const csky_rfft_instance_q15 *S, q15_t *pSrc, q15_t *pDst) |
| Processing function for the Q15 RFFT/RIFFT. More... | |
| void | csky_rfft_q31 (const csky_rfft_instance_q31 *S, q31_t *pSrc, q31_t *pDst) |
| Processing function for the Q31 RFFT/RIFFT. More... | |
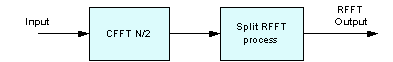
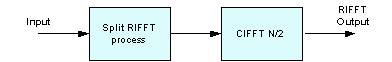
csky_rfft_fast_f32() and csky_rfft_fast_init_f32(). The older functions csky_rfft_f32() and csky_rfft_init_f32() have been deprecated but are still documented. *X[0] - real data *X[1] - complex data *X[2] - complex data *... *X[fftLen/2-1] - complex data *X[fftLen/2] - real data *X[fftLen/2+1] - conjugate of X[fftLen/2-1] *X[fftLen/2+2] - conjugate of X[fftLen/2-2] *... *X[fftLen-1] - conjugate of X[1]Looking at the data, we see that we can uniquely represent the FFT using only
*N/2+1 samples: *X[0] - real data *X[1] - complex data *X[2] - complex data *... *X[fftLen/2-1] - complex data *X[fftLen/2] - real dataLooking more closely we see that the first and last samples are real valued. They can be packed together and we can thus represent the FFT of an N-point real sequence by N/2 complex values:
*X[0],X[N/2] - packed real data: X[0] + jX[N/2] *X[1] - complex data *X[2] - complex data *... *X[fftLen/2-1] - complex dataThe real FFT functions pack the frequency domain data in this fashion. The forward transform outputs the data in this form and the inverse transform expects input data in this form. The function always performs the needed bitreversal so that the input and output data is always in normal order. The functions support lengths of [32, 64, 128, ..., 4096] samples.
*csky_rfft_instance_q31 S = {fftLenReal, fftLenBy2, ifftFlagR, bitReverseFlagR, twidCoefRModifier, pTwiddleAReal, pTwiddleBReal, pCfft};
*csky_rfft_instance_q15 S = {fftLenReal, fftLenBy2, ifftFlagR, bitReverseFlagR, twidCoefRModifier, pTwiddleAReal, pTwiddleBReal, pCfft};
where fftLenReal is the length of the real transform; fftLenBy2 length of the internal complex transform. ifftFlagR Selects forward (=0) or inverse (=1) transform. bitReverseFlagR Selects bit reversed output (=0) or normal order output (=1). twidCoefRModifier stride modifier for the twiddle factor table. The value is based on the FFT length; pTwiddleARealpoints to the A array of twiddle coefficients; pTwiddleBRealpoints to the B array of twiddle coefficients; pCfft points to the CFFT Instance structure. The CFFT structure must also be initialized. Refer to csky_cfft_radix4_f32() for details regarding static initialization of the complex FFT instance structure. | csky_status csky_cfft_radix4_init_f32 | ( | csky_cfft_radix4_instance_f32 * | S, |
| uint16_t | fftLen, | ||
| uint8_t | ifftFlag, | ||
| uint8_t | bitReverseFlag | ||
| ) |
| [in,out] | *S | points to an instance of the floating-point CFFT/CIFFT structure. |
| [in] | fftLen | length of the FFT. |
| [in] | ifftFlag | flag that selects forward (ifftFlag=0) or inverse (ifftFlag=1) transform. |
| [in] | bitReverseFlag | flag that enables (bitReverseFlag=1) or disables (bitReverseFlag=0) bit reversal of output. |
fftLen is not a supported value.ifftFlag controls whether a forward or inverse transform is computed. Set(=1) ifftFlag for calculation of CIFFT otherwise CFFT is calculated bitReverseFlag controls whether output is in normal order or bit reversed order. Set(=1) bitReverseFlag for output to be in normal order otherwise output is in bit reversed order. fftLen Specifies length of CFFT/CIFFT process. Supported FFT Lengths are 16, 64, 256, 1024. | void csky_rfft_fast_f32 | ( | csky_rfft_fast_instance_f32 * | S, |
| float32_t * | p, | ||
| float32_t * | pOut, | ||
| uint8_t | ifftFlag | ||
| ) |
| [in] | *S | points to an csky_rfft_fast_instance_f32 structure. |
| [in] | *p | points to the input buffer. |
| [in] | *pOut | points to the output buffer. |
| [in] | ifftFlag | RFFT if flag is 0, RIFFT if flag is 1 |
| csky_status csky_rfft_fast_init_f32 | ( | csky_rfft_fast_instance_f32 * | S, |
| uint16_t | fftLen | ||
| ) |
| [in,out] | *S | points to an csky_rfft_fast_instance_f32 structure. |
| [in] | fftLen | length of the Real Sequence. |
fftLen is not a supported value.fftLen Specifies length of RFFT/CIFFT process. Supported FFT Lengths are 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, 2048, 4096. | csky_status csky_rfft_init_f32 | ( | csky_rfft_instance_f32 * | S, |
| csky_cfft_radix4_instance_f32 * | S_CFFT, | ||
| uint32_t | fftLenReal, | ||
| uint32_t | ifftFlagR, | ||
| uint32_t | bitReverseFlag | ||
| ) |
| [in,out] | *S | points to an instance of the floating-point RFFT/RIFFT structure. |
| [in,out] | *S_CFFT | points to an instance of the floating-point CFFT/CIFFT structure. |
| [in] | fftLenReal | length of the FFT. |
| [in] | ifftFlagR | flag that selects forward (ifftFlagR=0) or inverse (ifftFlagR=1) transform. |
| [in] | bitReverseFlag | flag that enables (bitReverseFlag=1) or disables (bitReverseFlag=0) bit reversal of output. |
fftLenReal is not a supported value.fftLenReal Specifies length of RFFT/RIFFT Process. Supported FFT Lengths are 128, 512, 2048. ifftFlagR controls whether a forward or inverse transform is computed. Set(=1) ifftFlagR to calculate RIFFT, otherwise RFFT is calculated. bitReverseFlag controls whether output is in normal order or bit reversed order. Set(=1) bitReverseFlag for output to be in normal order otherwise output is in bit reversed order. | csky_status csky_rfft_init_q15 | ( | csky_rfft_instance_q15 * | S, |
| uint32_t | fftLenReal, | ||
| uint32_t | ifftFlagR, | ||
| uint32_t | bitReverseFlag | ||
| ) |
| [in,out] | *S | points to an instance of the Q15 RFFT/RIFFT structure. |
| [in] | fftLenReal | length of the FFT. |
| [in] | ifftFlagR | flag that selects forward (ifftFlagR=0) or inverse (ifftFlagR=1) transform. |
| [in] | bitReverseFlag | flag that enables (bitReverseFlag=1) or disables (bitReverseFlag=0) bit reversal of output. |
fftLenReal is not a supported value.fftLenReal Specifies length of RFFT/RIFFT Process. Supported FFT Lengths are 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, 2048, 4096, 8192. ifftFlagR controls whether a forward or inverse transform is computed. Set(=1) ifftFlagR to calculate RIFFT, otherwise RFFT is calculated. bitReverseFlag controls whether output is in normal order or bit reversed order. Set(=1) bitReverseFlag for output to be in normal order otherwise output is in bit reversed order. | csky_status csky_rfft_init_q31 | ( | csky_rfft_instance_q31 * | S, |
| uint32_t | fftLenReal, | ||
| uint32_t | ifftFlagR, | ||
| uint32_t | bitReverseFlag | ||
| ) |
| [in,out] | *S | points to an instance of the Q31 RFFT/RIFFT structure. |
| [in] | fftLenReal | length of the FFT. |
| [in] | ifftFlagR | flag that selects forward (ifftFlagR=0) or inverse (ifftFlagR=1) transform. |
| [in] | bitReverseFlag | flag that enables (bitReverseFlag=1) or disables (bitReverseFlag=0) bit reversal of output. |
fftLenReal is not a supported value.fftLenReal Specifies length of RFFT/RIFFT Process. Supported FFT Lengths are 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, 2048, 4096, 8192. ifftFlagR controls whether a forward or inverse transform is computed. Set(=1) ifftFlagR to calculate RIFFT, otherwise RFFT is calculated. bitReverseFlag controls whether output is in normal order or bit reversed order. Set(=1) bitReverseFlag for output to be in normal order otherwise output is in bit reversed order. | void csky_rfft_q15 | ( | const csky_rfft_instance_q15 * | S, |
| q15_t * | pSrc, | ||
| q15_t * | pDst | ||
| ) |
| [in] | *S | points to an instance of the Q15 RFFT/RIFFT structure. |
| [in] | *pSrc | points to the input buffer. |
| [out] | *pDst | points to the output buffer. |
| RFFT Size | Input Format | Output Format | Number of bits to upscale |
|---|---|---|---|
| 32 | 1.15 | 5.11 | 4 |
| 64 | 1.15 | 6.10 | 5 |
| 128 | 1.15 | 7.9 | 6 |
| 256 | 1.15 | 8.8 | 7 |
| 512 | 1.15 | 9.7 | 8 |
| 1024 | 1.15 | 10.6 | 9 |
| 2048 | 1.15 | 11.5 | 10 |
| 4096 | 1.15 | 12.4 | 11 |
| 8192 | 1.15 | 13.3 | 12 |
| RIFFT Size | Input Format | Output Format | Number of bits to upscale |
|---|---|---|---|
| 32 | 1.15 | 5.11 | 0 |
| 64 | 1.15 | 6.10 | 0 |
| 128 | 1.15 | 7.9 | 0 |
| 256 | 1.15 | 8.8 | 0 |
| 512 | 1.15 | 9.7 | 0 |
| 1024 | 1.15 | 10.6 | 0 |
| 2048 | 1.15 | 11.5 | 0 |
| 4096 | 1.15 | 12.4 | 0 |
| 8192 | 1.15 | 13.3 | 0 |
| void csky_rfft_q31 | ( | const csky_rfft_instance_q31 * | S, |
| q31_t * | pSrc, | ||
| q31_t * | pDst | ||
| ) |
| [in] | *S | points to an instance of the Q31 RFFT/RIFFT structure. |
| [in] | *pSrc | points to the input buffer. |
| [out] | *pDst | points to the output buffer. |
| RFFT Size | Input Format | Output Format | Number of bits to upscale |
|---|---|---|---|
| 32 | 1.31 | 5.27 | 4 |
| 64 | 1.31 | 6.26 | 5 |
| 128 | 1.31 | 7.25 | 6 |
| 256 | 1.31 | 8.24 | 7 |
| 512 | 1.31 | 9.23 | 8 |
| 1024 | 1.31 | 10.22 | 9 |
| 2048 | 1.31 | 11.21 | 10 |
| 4096 | 1.31 | 12.20 | 11 |
| 8192 | 1.31 | 13.19 | 12 |
| RIFFT Size | Input Format | Output Format | Number of bits to upscale |
|---|---|---|---|
| 32 | 1.31 | 5.27 | 0 |
| 64 | 1.31 | 6.26 | 0 |
| 128 | 1.31 | 7.25 | 0 |
| 256 | 1.31 | 8.24 | 0 |
| 512 | 1.31 | 9.23 | 0 |
| 1024 | 1.31 | 10.22 | 0 |
| 2048 | 1.31 | 11.21 | 0 |
| 4096 | 1.31 | 12.20 | 0 |
| 8192 | 1.31 | 13.19 | 0 |