|
CSI-DSP
Version 1.0.0
CSI DSP Software Library
|
|
CSI-DSP
Version 1.0.0
CSI DSP Software Library
|
Functions | |
| csky_status | csky_mat_inverse_f32 (const csky_matrix_instance_f32 *pSrc, csky_matrix_instance_f32 *pDst) |
| Floating-point matrix inverse. More... | |
| csky_status | csky_mat_inverse_f64 (const csky_matrix_instance_f64 *pSrc, csky_matrix_instance_f64 *pDst) |
| Floating-point matrix inverse. More... | |
Computes the inverse of a matrix.
The inverse is defined only if the input matrix is square and non-singular (the determinant is non-zero). The function checks that the input and output matrices are square and of the same size.
Matrix inversion is numerically sensitive and the CSI DSP library only supports matrix inversion of floating-point matrices.
CSKY_MATH_SINGULAR. 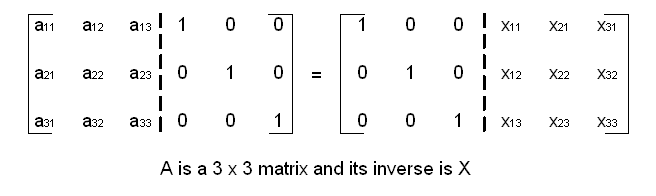
| csky_status csky_mat_inverse_f32 | ( | const csky_matrix_instance_f32 * | pSrc, |
| csky_matrix_instance_f32 * | pDst | ||
| ) |
| [in] | *pSrc | points to input matrix structure |
| [out] | *pDst | points to output matrix structure |
CSKY_MATH_SIZE_MISMATCH if the input matrix is not square or if the size of the output matrix does not match the size of the input matrix. If the input matrix is found to be singular (non-invertible), then the function returns CSKY_MATH_SINGULAR. Otherwise, the function returns CSKY_MATH_SUCCESS. | csky_status csky_mat_inverse_f64 | ( | const csky_matrix_instance_f64 * | pSrc, |
| csky_matrix_instance_f64 * | pDst | ||
| ) |
| [in] | *pSrc | points to input matrix structure |
| [out] | *pDst | points to output matrix structure |
CSKY_MATH_SIZE_MISMATCH if the input matrix is not square or if the size of the output matrix does not match the size of the input matrix. If the input matrix is found to be singular (non-invertible), then the function returns CSKY_MATH_SINGULAR. Otherwise, the function returns CSKY_MATH_SUCCESS.